Kaggle 课程(一)
线性模型
Tree-based: Deceision Tree, Random Forest, GBDT 推荐(XGBoost和LightGBM,收敛速度快, 准确性较高), 算法需要去理解
缺点:由于基于树得结构需要大量的分裂,因此很难捕捉到数据的线性相关性
KNN-based:
Neural Networks
可以安装的python包: vowpal wabbit : libfm, libffm, fast_rgf(集成方法),
特征数据加工与提取概略
1、特征预处理 2、特征生成 3、Their dependence on a model type 前两者取决于你要用的模型
数字特征的加工与提取(Numerice feature)
1、预处理:正规化(regularization to linear model coefficients for features in equal amount) ==> 由于线性模型和神经网络模都型对特征的正规化有要求,因此这两个模型更为相似
1)、scaling a、To [0,1] min-max scaling sklearn.proprocessing.MinMaxScaler b、 To mean=0, std=1 sklearn.proprocessing.StandardScaler
特征缩放的影响对于非基于树模型的影响是大致相同的 2)、outliers 离群点 a、 极值调整
3)rank 使用数据的索引而不是数据本省,KDD和神经网络受益于此方法 秩 scipy.stats.rankdata rank([-100,0,1e5]) = [0,1,2] rank([1000,1, 10]) = [2,0,1] 在训练前,将train和test数据组成起来,然后再进行rank处理
数据变换 4)Log transform np.log(1+x)
5)Raising to the power < 1 np.sqrt(x + 2/3)
feature generation
1、prior knowledge 2、EDA (exploratory data analysis)
conclusion
1、Numeric feature preprocessing is different for tree and non-tree models: a、Tree-based models doesn’t depend on scaling b、Non-tree-based models hugely depend on scaling
类别特征与顺序特征的加工和提取 (Categorical and ordinal features)
如泰坦尼克号比赛中,pclass说明了船仓的等级,1,2,3;这些具有特殊的意义,所以应该对这些数据进行说明或描述 (1)Ordinal features (序数特征) => label encoding Ticket class: 1,2,3 Driver’s license:A,B,C,D Education: kindergarden, school, undergraduate, bachelor, master, doctoral
1、Label encoding vector: embarked S, C, S, S, … a)Alphabetical (sorted) [S,C,Q] => [2,1,3] sklearn.preprocessing.LabelEncoder b)Order of appearance [S,C,Q] => [1,2,3] Pandas.factorize
2、Frequency encoding [S,C,Q] => [0.5, 0.3, 0.2] encoding = titanic.groupby(‘Embarked’).size() encoding = encoding / len(titanic) titanic[‘enc’] = titanic.Embarked.map(encoding) from scipy.stats import rankdata (2) Categorical features 1、one-hot encoding => 稀疏矩阵 常用于非树模型
Conclusion
1、Values in ordinal features are sorted in some meaningful order 2、Label encoding maps categories to numbers 3、Frequency encoding maps categories to their frequencies 4、Label and Frequency encodings are often used for tree-based models 5、One-hot encoding is often used for non-tree-based models 6、Interactions of categories features can help linear models and KNN
时间特征与位置特征的提取和加工(Datetime and coordinates)
1、Date and time Day number in week, month, season, year, second, mintue, hour 1) Periodicity 2) Time Since a、Row-independent moment For example: since 00:00:00 UTC,1 Januray 1970; b、Row-dependent import moment Number of days lefet until next holidays/time passed after last holiday. 3) Difference between dates datetime_feature_1 - datetime_feature_2
2、 competitions with coordinates)
1) Interesting places from train/test data or additional data 考虑附件的显著性的建筑物等,如到医院、最好学院、广场的距离。 或房价等(距离, 汇总统计) 2) Centers of clusters 3) Aggregated statistics
Missing values 处理丢失数据 Handing Missing values
 1、Missing data, numberic Hidden NaNs 缺失值可以用一些有意义的词替代
1、Missing data, numberic Hidden NaNs 缺失值可以用一些有意义的词替代
1)Fillna approaches 1、 -999, -1, etc 将缺失值映射到一个新值上,缺点是可能使基于线性神经网络性能下降 2、mean, median 有益于简单的线性模型和神经网络, 基于树模型 3、 Reconstruct value
时间序列中的缺失值,例如某月的几天气温的数据消失, 那么使用附近的几行数据进行重建(如果缺失值的范围较大,则在fillna 时应该格外小心) 3)“Isnull” feature
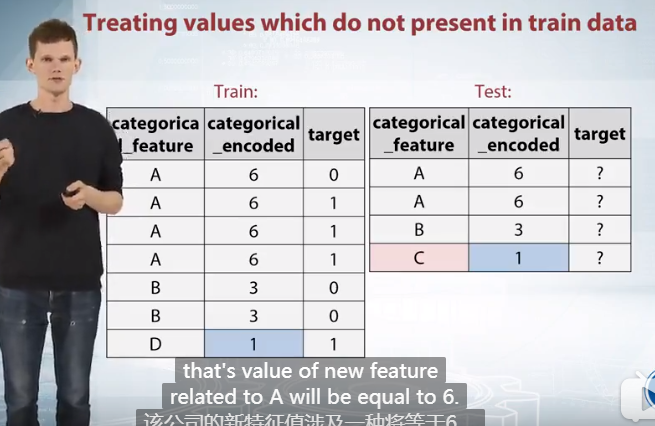
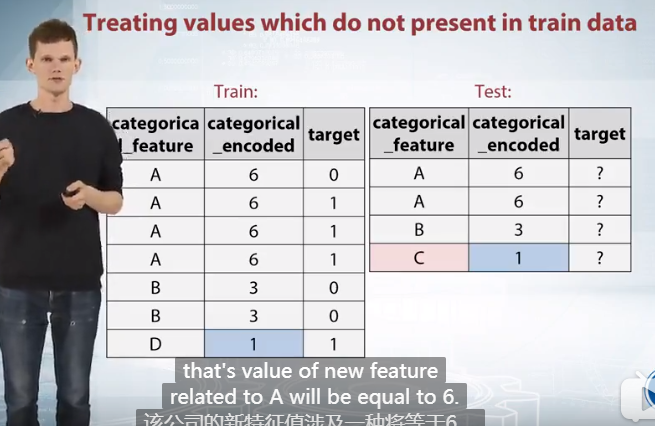
Treating values which do not present in train data 计算特征在训练集和测试集共出现的频率,然后使用不同特征的频率作为新的特征
Treating values which do not present in train data
- The choice of method to fill NaN depends on the situation
- Usual way to deal with missing value is to replace them with -999, mean or median
- Missing values already can be replaced with something by organizers 通过查看此类的直方图
- Binary feature ‘isnull’ can be beneficial
- In general, avoid filling nans before feature generation (数据丢失)
- Xgboost can handle NaNs
Featurre extraction from texts and images 文字特征的提取—词袋模型 Bag of words
 1、Text -> vector a). Bag of words sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer TFiDF 1)Term frequency tf = 1 / x.sum(axis=1)[:,None] x = x* tf 2)Inverse Document Frequency idf = np.log(x.shape(0) / (x>0).usm(0)) x = x * idf sklearn.feature_extraction.TfidVectorizer 通用频率和inverse文档频率转换 3)N-grams sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer: Ngram_range, analyzer b). Embedding
1、Text -> vector a). Bag of words sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer TFiDF 1)Term frequency tf = 1 / x.sum(axis=1)[:,None] x = x* tf 2)Inverse Document Frequency idf = np.log(x.shape(0) / (x>0).usm(0)) x = x * idf sklearn.feature_extraction.TfidVectorizer 通用频率和inverse文档频率转换 3)N-grams sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer: Ngram_range, analyzer b). Embedding
2、Text preprocessing 1.Lowercase 2.Lemmatization 词性还原 I had a car => i have car democracy, democratic, and democratization -> democracy Saw -> see or saw(depending on context) 3.Stemming 词干 we have cars -> we have car democracy, democratic, and democratization -> democr Saw->s 4.Stopwords 停用词 NLTK, Nature Language Toolkit library for python sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer; max_df ,即希望从文本中删除的文字或单词
Conclusion
Pipeline of applying BOW 1.Preprocessing: Lowercase, stemming, Lemmatization, stopwords
- N-grams can help to use local context 3.Postprocessing:TFiDF
文本特征的提取—-词向量与卷积 CNN word2vector && CNN
- Text -> vector (comparison)两者在比赛中可以共同使用 1). Bags of words a. very large vectors b. Meaning of each value in vector is known 2).Embedding(~word2vec) a. Relatively small vector b.Values in vector can be interpreted only in some cases(drawback) c. The words with similar meaning often have similar embeddings a) Word2vec Word: word2vec, Glove, FastText, etc Sentences:Doc2vec, etc
- Image -> vector 1). Descriptors 2). Train network from scratch 3).Finetuning finetuning is better than training on standalone model on descriptors because it allows to tun all networks parameters and than extract more effective image representations (使用预训练模型,改变输出层)
Augmentation (旋转) gruop, rotations, and the noise and so on.
Feature extraction from text and images
- Texts 1).Preprocessing Lowercase, Stemming, Lemmatization, Stopwords 2). Bag of words a. Huge vector b. N-grams can help to use local context c. TFiDF can be of use as postprocessing 3). Word2vec a. Relatively small vectors b. Pretrained models
- Images a. Features can be extracted from different layers b. Careful choosing of pretrained network can help c. Finetuning allows to refine pretrained models d. Data augmentation can improve the model